What Colors Are The Two Stars At The Head Of Cygnus?
Cygnus is a prominent constellation in the northern heaven. Its name ways "the swan" in Latin and information technology is also known as the Swan constellation.
Cygnus is associated with the myth of Zeus and Leda in Greek mythology. The constellation is piece of cake to notice in the sky as information technology features a well-known asterism known every bit the Northern Cross. Cygnus was first catalogued the by Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the 2nd century.
Notable objects in the constellation include Cygnus X-i, a famous 10-ray source, the vivid stars Deneb and Albireo, the yellow dwarf Kepler-22, which hosts the exoplanet Kepler-22b, the Fireworks Galaxy (NGC 6946), and several well-known nebulae: the Cocoon Nebula (IC 5146), the Precious stone Problems Nebula (NGC 7027), the Pelican Nebula (IC 5070), the Northward America Nebula (NGC 7000), the Crescent Nebula (NGC 6888), Sadr Region (IC 1318) and the Veil Nebula (NGC 6960, 6962, 6979, 6992, and 6995).
Facts, location and map
Cygnus is the 16th largest constellation in the dark sky, occupying an area of 804 foursquare degrees. It lies in the fourth quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ4) and can exist seen at latitudes between +90° and -40°. The neighboring constellations are Cepheus, Draco, Lacerta, Lyra, Pegasus, and Vulpecula.
Cygnus belongs to the Hercules family of constellations, along with Aquila, Ara, Centaurus, Corona Australis, Corvus, Crater, Crux, Hercules, Hydra, Lupus, Lyra, Ophiuchus, Sagitta, Scutum, Sextans, Serpens, Triangulum Australe, and Vulpecula.
Cygnus has 10 stars with known planets and contains two Messier objects: Messier 29 (NGC 6913) and Messier 39 (NGC 7092). The brightest star in the constellation is Deneb, Alpha Cygni, which is also the 19th brightest star in the sky, with an credible magnitude of 1.25. There are two shooting star showers associated with the constellation: the October Cygnids and the Kappa Cygnids.
Cygnus contains 6 named stars. The proper names of stars that have been officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) are Albireo, Aljanah, Azelfafage, Deneb, Fawaris, and Sadr.

Cygnus, image: Constellation Guide
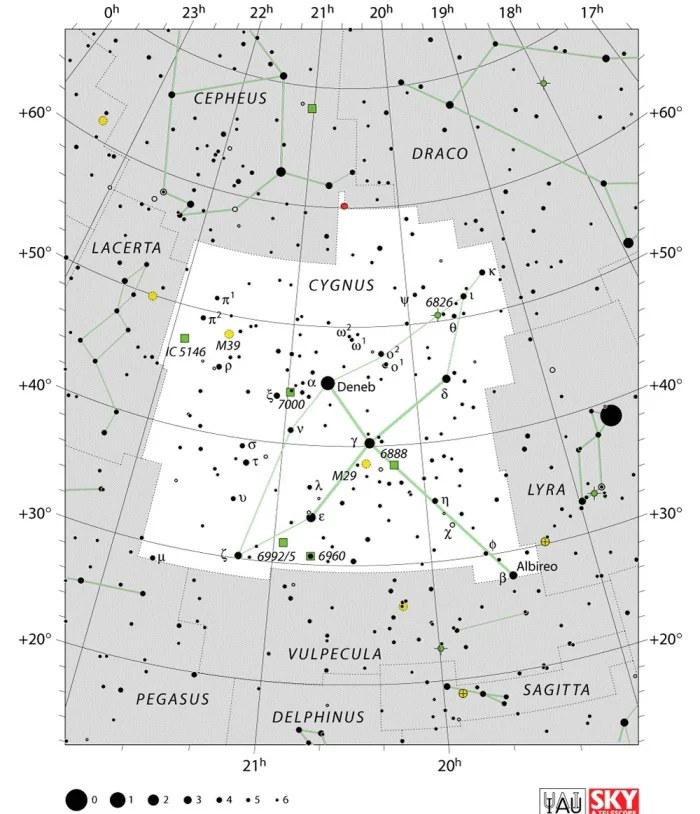
Cygnus constellation map by IAU and Sky&Telescope mag
Cygnus myth
Cygnus constellation is associated with several myths, almost frequently the ane of the Spartan Queen Leda, who gave nascence to two sets of twins, the immortal Pollux and Helen and mortal Castor and Clytemnestra, after being seduced by the god Zeus, who had transformed himself into a swan. The immortal children were fathered by the god and the mortal ones by Leda's husband, King Tyndareus. Castor and Pollux are represented by the zodiac constellation Gemini.
Cygnus is too sometimes identified as Orpheus, the Greek tragic hero who met his finish at the easily of the Thracian Maenads for not honouring Dionysus. After his passing, Orpheus was transformed into a swan and placed side by side to his lyre in the sky. The lyre is represented past the neighbouring constellation Lyra.
Cygnus constellation is also sometimes associated with any of the several people called Cycnus in Greek mythology. The most famous ones are Cycnus, the son of Ares who met his end afterward challenging Hercules to a duel, Cycnus, the son of Poseidon, who fought on the side of the Trojans in the Trojan War, met his end at the hands of Achilles and was transformed into a swan, and Cycnus, a close friend of Phaeton, the mortal son of the Sun god Helios. Of the above three, the myth of Phaeton is the one that is nearly frequently associated with Cygnus constellation.
In the story, Phaeton and Cycnus were racing each other across the sky when they came too close to the Sunday. Their chariots burned up and they fell to the Globe. Cycnus came to and, after looking for Phaeton for a while, he discovered his friend's body trapped at the bottom of the Eridanus River. He was unable to recover the trunk, then he made a pact with Zeus: if the god gave him the torso of a swan, he would just live as long as a swan usually does. Once transformed, Cycnus was able to dive into the river, remember Phaeton's body and give his friend a proper burial. This allowed Phaeton's soul to travel to the afterlife. Zeus was moved by Cycnus' sacrifice and placed his image in the sky.
The Chinese also acquaintance the constellation with a myth, the one of the "magpie bridge," Que Qiao. In the story, the lovers Niu Lang and Zhi Nu are separated by the Goddess of Heaven because Zhi Nu is a fairy, and is therefore not immune to be with a mortal human. When the Goddess learns that the two are secretly married, she takes Zhi Nu with her and creates a river in the sky to keep the lovers separated. The river is represented by the Galaxy itself in the fable. Zhi Nu's married man Niu Lang takes their 2 children to Heaven so that they tin can all be together, just the Goddess does non relent and keeps the lovers separated. In one case a year, the myth goes, all the magpies in the world assemble to assist the lovers be together past forming an enormous bridge over the wide river. The constellation Cygnus represents the magpie span in this story.
Asterisms
Northern Cross
The five stars that form the Northern Cross are Deneb (Alpha Cygni), Fawaris (Delta Cygni), Albireo (Beta Cygni), Aljanah (Epsilon Cygni) and Sadr (Gamma Cygni) at the heart.
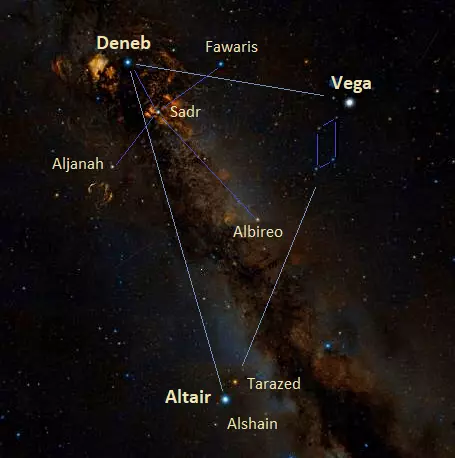
The Summer Triangle and the Northern Cantankerous, image: Wikisky
Cygnus stars
Deneb – α Cygni (Alpha Cygni)
Deneb is a blue-white supergiant belonging to the spectral class A2 Ia, approximately 1,400 light years distant. It is the brightest star in Cygnus and the 19th brightest star in the night sky. It has an apparent magnitude of 1.25. With an absolute magnitude of -seven.0, Deneb is one of the most luminous stars known. It is about 60,000 times more luminous than our Sun and has most 20 solar masses. While it is difficult to get an accurate distance, Deneb is even so the most distant star that shines at first magnitude. Information technology is also one of the largest white stars known. On Mars, Deneb is the North Pole star.
Deneb serves as a image for a course of variable stars known as the Alpha Cygni variables. Its brightness and spectral type fluctuate slightly as a upshot of non-radial fluctuations of the star's surface. Deneb has stopped fusing hydrogen in its core and is expected to go out as a supernova inside the next few meg years.
The proper noun Deneb comes from the Arabic dhaneb, meaning "tail," from the phrase Dhanab ad-Dajājah, which means "the tail of the hen." In the Chinese myth of the magpie bridge, Deneb marks the bridge or, alternatively, it represents a fairy who chaperones the ii lovers when they meet one time a twelvemonth.
Together with the brilliant stars Altair in the constellation Aquila (the Eagle) and Vega in Lyra, Deneb forms the Summertime Triangle, a prominent asterism in the summer sky.
Sadr – γ Cygni (Gamma Cygni)
Gamma Cygni is the star located at the intersection of the Northern Cross. Its traditional name, Sadr, comes from the Arabic word for "the breast," şadr. It is besides sometimes known by its Latin name, Pectus Gallinae, which means "the hen's breast."

Sadr Region, prototype: Erik Larsen (CC BY two.0)
Gamma Cygni belongs to the spectral grade F8 lab (indicating that the star is a supergiant) and it is approximately one,800 light years distant from Globe. It has an apparent magnitude of 2.23 and is one of the brightest stars that tin can be seen in the dark sky. It has twelve solar masses and a radis 150 times solar. Gamma Cygni is believed to be simply about 12 meg years one-time. It consumes its nuclear fuel more than quickly because of its mass.
Gamma Cygni is surrounded by a diffuse emission nebula, IC 1318, also known equally the Sadr region or the Gamma Cygni region.
Aljanah – ε Cygni (Epsilon Cygni)
Aljanah, Epsilon Cygni, is an orange giant star of the spectral blazon K0 III. It has an apparent magnitude of ii.480 and is 72.7 light years distant. Information technology is 62 times more than luminous than the Sun and has has a radius xi times solar.
Epsilon Cygni historically shared the traditional name Gienah with Gamma Corvi in the constellation Corvus. However, the International Astronomical Wedlock (IAU) approved the name Aljanah for the star in 2017, while Gamma Corvi has kept the name Gienah. Both names come from the Standard arabic word janāħ, which means "the wing." Both stars mark the wings of their corresponding birds.
Aljanah has a 13th magnitude line-of-sight companion.
Fawaris – δ Cygni (Delta Cygni)
Delta Cygni is a triple star in Cygnus. Information technology volition take over as the Due north Star for at least 400 years around the year eleven,250. The star arrangement has a combined apparent magnitude of two.87 and is approximately 165 light years distant.
The Delta Cygni system consists of two stars lying shut together and a star located a scrap further from the main pair. The brightest component in the system is a blue-white giant belonging to the spectral class B9 III, which is approaching the final stages of life on the main sequence. It is a fast rotating star, with an equatorial speed of at least 135 kilometres per second.
The star'due south closer companion is a yellow-white star belonging to the spectral class F1 5 with an credible magnitude of 6.33. The third component in the Delta Cygni system is a 12th magnitude orange behemothic.
Albireo – β Cygni (Beta Cygni)
Albireo, Beta Cygni, is merely the 5th brightest star in the constellation Cygnus. It is a binary star system that appears equally a single third magnitude star to the unaided eye. The system is approximately 380 light years distant.
Albireo marks the caput of the swan and is sometimes also known as "the beak star." It is one of the stars that form the Northern Cross.
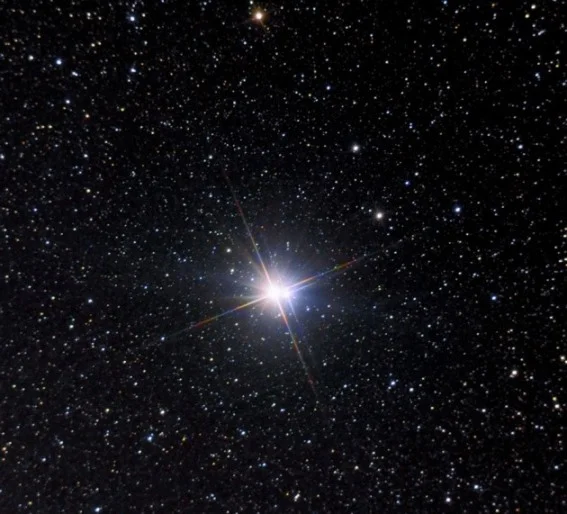

Albireo A, image: Henryk Kowalewski
Albireo is equanimous of a yellowish star with an apparent magnitude of 3.18, which is in fact itself a shut binary star, and a fainter blue companion star with an apparent magnitude of 5.82. The components are located 35 arc seconds apart. The contrast between the stars makes Albireo a pretty pop target amongst amateur astronomers.
Albireo A, the brighter component, consists of ii stars simply 9.4 arc seconds apart, which cannot exist resolved with telescopes less than 20'' in size. The system belongs to the spectral form K3III.
Albireo B belongs to the spectral blazon B0V and is a fast-rotating Exist star, with an estimated rotational velocity of 250 kilometres per 2d.
ζ Cygni (Zeta Cygni)
Zeta Cygni is a yellow star belonging to the spectral class G8III, approximately 151 light years distant. Information technology has an apparent magnitude of iii.20. Its radius is 14.7 times solar, and the star is 119 times brighter than the Sun. It is believed to a core-helium fusing giant. The star has a 12th magnitude companion believed to be a white dwarf.
Zeta Cygni and the star CCDM J21129+3014B form a binary system.
τ Cygni (Tau Cygni)
Tau Cygni is a double star in Cygnus. It is composed of a yellowish white subgiant star, GJ 822.ane A, which belongs to the spectral course F2IV, and a sixth magnitude companion, GJ 822.one B, a yellow main sequence star of the spectral type G0V. The companion has a similar size, luminosity and surface temperature equally the Lord's day.
Tau Cygni's components have apparent magnitudes of iii.84 and 6.44. The organization is 68.2 light years distant from the solar organisation.
κ Cygni (Kappa Cygni)
Kappa Cygni is a giant star of the spectral type G9 III. It has an credible magnitude of 3.814 and is 124.2 calorie-free years distant from Globe. The star marks the tip of the swan'due south left wing. It can exist seen without binoculars.
Kappa Cygni is besides notable for the falling star shower associated with it. The Kappa Cygnids meteor shower (KCG) can be observed virtually five degrees north of the star. It is a minor meteor shower that takes place in August every year.
η Cygni (Eta Cygni)
Eta Cygni is an orangish giant, belonging to the spectral course K0III, approximately 139 light years distant. Information technology has an credible magnitude of iii.909.
π Cygni (Pi Cygni)
Pi Cygni consists of two star systems. Pi-1 Cygni belongs to the spectral type B3IV. Information technology has a visual magnitude of 4.67 and is 1680 light years distant. Its traditional name, Azelfafage, comes either from the Arabic phrase al thīlf al faras, which means "the equus caballus track" or from al ʽazal al-dajājah, "the hen's tail."
Pi-two Cygni has a magnitude of 4.23 and is approximately 1156 light years afar. It is a spectroscopic binary star whose master component is a B3-type blue behemothic, virtually 2,200 times more luminous than the Sunday.
Pi-2 Cygni has a couple of traditional names: Pennae Caudalis, which ways "tail fathers" in Latin, and Sama al Azrak, which is Arabic for "the blueish sky."
Bessel's Star (Piazzi's Falling Star) – 61 Cygni
61 Cygni is a double star organisation composed of a pair of two dwarfs belonging to the spectral types K5V and K7V, which orbit each other every 659 years. They have credible magnitudes of v.21 and half dozen.03 respectively. 61 Cygni is only xi.41 light years distant from the solar system. Information technology is the 15th nearest known star organisation to Earth.

61 Cygni (Bessel'southward Star), prototype: Wikisky
61 Cygni A, the brighter component in the system, is the 4th nearest visible star, subsequently Sirius in Canis Major, Epsilon Eridani in Eridanus, and Procyon A in Canis Minor. It will come inside nine light years of the solar organisation around the twelvemonth xx,000.
61 Cygni is notable for its big proper movement, the angular change in position over the course of fourth dimension, equally observed from the solar system's centre of mass. The star's proper motion was originally demonstrated by the Italian astronomer and mathematician Giuseppe Piazzi in 1804. He named 61 Cygni the Flying Star.
61 Cygni is the offset star other than the Sun to have its distance from World measured. The German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel did this using the method of parallax, measuring the displacement of the star's apparent position observed along two dissimilar lines of sight and the bending of inclination between the two. The star'southward large proper motion made it a cracking candidate for this.
34 Cygni (P Cygni)
P Cygni is a variable star classified equally a hypergiant luminous blue variable (LBV). Luminous blue variables are rare and merely found in regions of intense star formation. They are usually curt lived. Because of their enormous mass and free energy, they exhaust their nuclear fuel pretty quickly and erupt into supernovae after but a few million years. Our Lord's day, for comparison, has been around for several billion years.
P Cygni belongs to the spectral class B1Ia+ and is approximately 6,000 low-cal years afar from World. It is one of the near luminous stars ever discovered in the Milky Way.
It was first observed by the Dutch astronomer Willem Janszoon Blaeu in August 1600. It had not been discovered sooner because information technology but brightened to third magnitude in the last few years of the 16th century. Information technology faded again in 1626 so brightened once again in 1655 only to fade again in 1662. The star'southward fluctuations in brightness became less dramatic effectually 1715. Information technology has been a fifth magnitude star always since. Today, information technology has an apparent magnitude of 4.8 with fluctuations up to 0.v magnitudes.
It was Johann Bayer who gave the star the designation P as a nova. P Cygni is sometimes chosen a permanent nova because of its dramatic changes in effulgence, even though the star's behaviour is not that of a true nova.
39 Cygni
39 Cygni is an orangish star belonging to the spectral class K3III. It has an apparent magnitude of 4.436 and is approximately 260 light years distant. It is cooler than the Sunday, but much brighter and larger. Its surface temperature is between 3,500 and 5,000 kelvin.
θ Cygni (Theta Cygni)
Theta Cygni is master sequence star belonging to the spectral course F3 V, approximately 59.8 light years afar from the solar system. Information technology has an apparent magnitude of 4.490. It is 4 times as luminous as our Dominicus and has about 38 percent more mass. It is betwixt 0.6 and one.9 billion years onetime.
The star has a faint companion, ane with a magnitude of thirteen.03, located near three arc seconds abroad. The companion is a red dwarf belonging to the spectral class M3 V.
Theta Cygni is too notable for mayhap having an extrasolar planet in its organisation. The ELODIE squad discovered radial velocity variations that propose that the star has a planetary object orbiting it with a catamenia of less than six months. The planet is believed to be twice the size of Jupiter, simply its presence has non been confirmed yet.
xvi Cygni
16 Cygni is a triple star organization in Cygnus. The brighter two components, two yellow dwarfs like to the Sun, have apparent magnitudes of five.96 and vi.20. The tertiary component is a red dwarf. The system is some 70 light years distant from World. An extrasolar planet has been discovered in an eccentric orbit around xvi Cygni B.
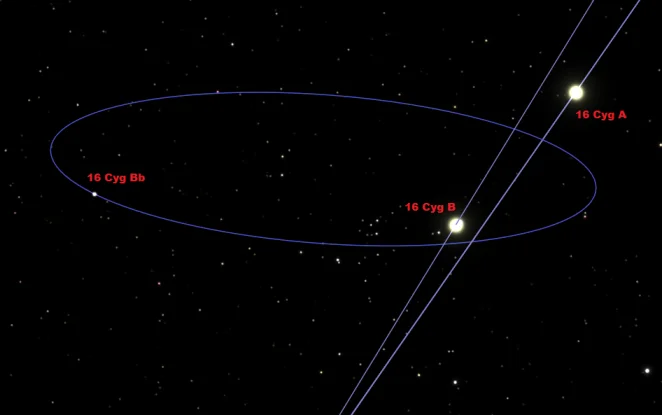
sixteen Cygni star system and orbits, photo: Arnaugir
Gliese 777
Gliese 777 is a yellow subgiant star belonging to the spectral class G6IV, 51.81 calorie-free years afar. Information technology has an apparent magnitude of v.71. In 2005, two extrasolar planets were confirmed in its arrangement.
The chief star has a companion, a dim red dwarf of the spectral type M4.5V, which is located approximately 3,000 astronomical units away. The ruby dwarf has a visual magnitude of 14.xl and is a suspected binary star.
Ruchba – ω Cygni (Omega Cygni)
Omega Cygni is a multiple star arrangement in Cygnus. It consists of two visual doubles only a 3rd of a caste apart. The star's traditional name, Ruchba, comes from the Standard arabic phrase meaning "the hen'due south knee." Omega-i Cygni is a hot subgiant belonging to the spectral course B2.five, approximately 910 calorie-free years afar. It has a visual magnitude of 4.95. Omega-ii Cygni is a ruby-red giant of the spectral type M2III approximately 400 light years from Earth. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.22.
Deep sky objects in Cygnus
Messier 29 (M29) – NGC 6913
Messier 29 is an open up cluster with an apparent magnitude of 7.1, approximately four,000 light years distant. It tin be seen with binoculars. The cluster was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764. It lies near the star Gamma Cygni, well-nigh 1.7 degrees to the southward and a little east.
The estimated age of the cluster is 10 million years. The brightest star has a visual magnitude of 8.59. The v hottest stars in the cluster belong to the spectral form B0.
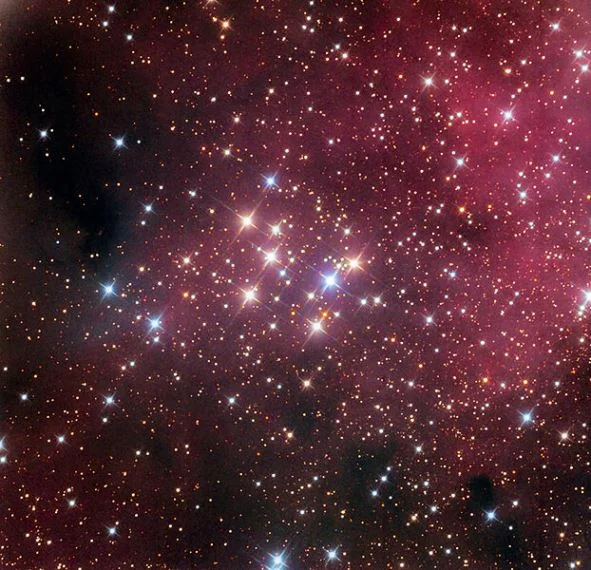

Messier 29, image: Adam Block/Mount Lemmon SkyCenter/University of Arizona (CC Past-SA three.0 Usa)
Messier 39 (M39) – NGC 7092
Messier 39 is another open up star cluster, too discovered by Charles Messier in 1764. Information technology is between 200 and 300 million years former, which is an intermediate age for an open cluster. The cluster is located nigh 800 light years from the solar system.
M39 has an apparent magnitude of v.5. The brightest star belongs to the spectral class A0 and has a visual magnitude of vi.83. All the stars observed in the cluster are on the main sequence, and the brightest ones will soon evolve to the scarlet giant stage.
The cluster can be found two and a half degrees due west and a caste s of the star Pi-2 Cygni.

Messier 39, prototype: Wikisky
Fireworks Galaxy – NGC 6946 (Arp 29)
The Fireworks Galaxy (NGC 6946) is an intermediate spiral galaxy in Cygnus. Information technology has an apparent magnitude of ix.6 and is approximately 22.5 million low-cal years distant.
The galaxy is located near the border with the constellation Cepheus. It lies close to the galactic plane and is very obscured by interstellar matter of the Milky Mode.
NGC 6946 was discovered by the German language-born British astronomer Sir Frederick William Herschel on September ix, 1798. 9 supernovae have been observed in the milky way since: SN 1917A, SN 1939C, SN 1948B, SN 1968D, SN 1969P, SN 1980K, SN 2002hh, SN 2004et and SN 2008S.
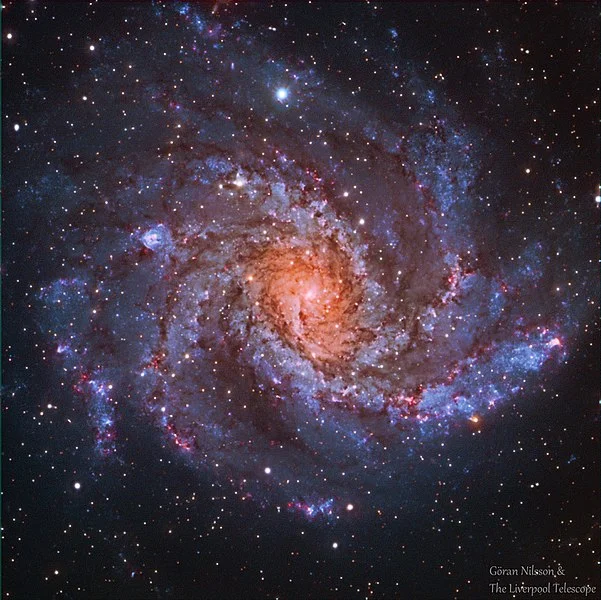

The Fireworks Galaxy (NGC 6946), image: Göran Nilsson & The Liverpool Telescope (CC BY-SA 4.0)
Cygnus X-ane
Cygnus X-1 is a famous X-ray source, 1 of the strongest ones seen from World. It was first discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight.
Cygnus 10-1 is notable for beingness the first Ten-ray source widely believed to be a black pigsty candidate; it has a mass eight.7 times that of the Sunday, withal it is as well compact to be any kind of known object other than a black hole. It is approximately 6,100 light years distant from Earth.
Cygnus X-1 orbits a bluish supergiant variable star, HDE 226868, and the two stars form a binary organisation. Over time, an accession disk of cloth brought from the star by a stellar wind has formed around Cygnus X-1.
North America Nebula – NGC 7000 (Caldwell 20)
NGC 7000 in Cygnus was named the North America Nebula because its shape strongly resembles that of the continent. The nebula is obscured past a band of dust, which determines its shape equally we see information technology.
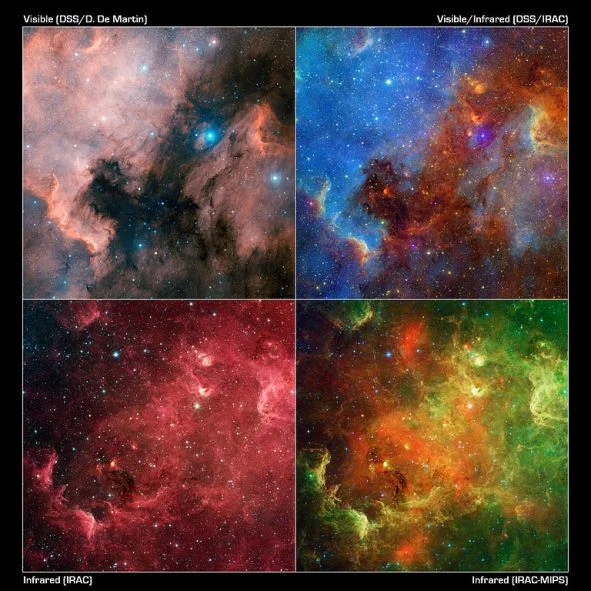

The North America Nebula and the Pelican Nebula — This layout of images reveals how the advent of the North America nebula tin can change dramatically using dissimilar combinations of visible and infrared observations from the Digitized Sky Survey and NASA's Spitzer Infinite Telescope, respectively. In this progression, the visible-light view (upper left) shows a striking similarity to the North America continent. Each is cropped to the easterly majority (thus besides the quasi-"Gulf of United mexican states" region). The red region to the right is known every bit the "Pelican nebula," after its resemblance in visible light to a pelican. The view at upper right includes both visible and infrared observations. The hot gas comprising the North America continent and the Pelican now takes on a vivid bluish hue, while red colours display the infrared light. Inky black dust features start to glow in the infrared view. In the bottom 2 images, only infrared light from Spitzer is shown — information from the infrared array photographic camera is on the left, and information from both the infrared array camera and the multi-band imaging photometer, which sees longer wavelengths, is on the right. These pictures look unlike in role considering infrared light can penetrate dust whereas visible light cannot. Dusty, dark clouds in the visible image become transparent in Spitzer'southward view. In addition, Spitzer's infrared detectors choice up the glow of dusty cocoons enveloping baby stars. Prototype: NASA/JPL-Caltech/L. Rebull (SSC/Caltech)
The North America Nebula is an emission nebula. It has an apparent magnitude of 4 and is approximately 1,600 light years afar from Earth.
The North America Nebula is very large, well-nigh 120 by 100 arc minutes, only it usually cannot exist seen without binoculars considering its surface brightness is pretty low. It was discovered by William Herschel on October 24, 1786.
The greatest concentration of star forming activity occurs in the region chosen the Cygnus Wall, which is the role of the nebula that corresponds to the Mexico and Fundamental America region (so to speak).
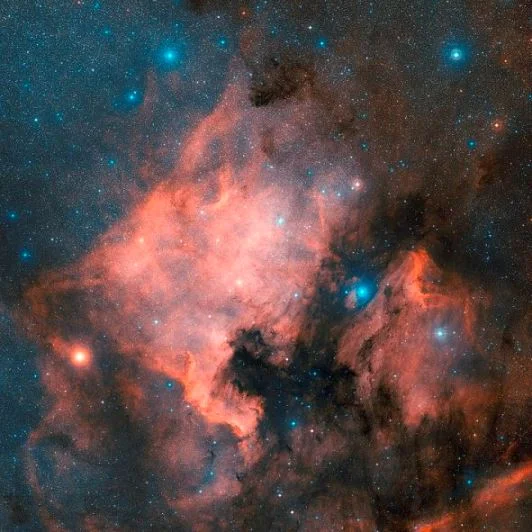

The N America Nebula and the Pelican Nebula, epitome: NASA
NGC 7000 is a office of the same H Ii region (interstellar deject in which stars are formed) as the neighbouring Pelican Nebula (IC 5070).
Pelican Nebula – IC 5070 and IC 5067
The Pelican Nebula is an emission nebula in Cygnus. It has an apparent magnitude of 8.0 and is approximately one,800 low-cal years afar from Earth. It got its proper name because its shape resembles that of the pelican.
The nebula is an H II region, a large gas cloud in which star forming action takes place and newly formed blue stars emit ultraviolet light which ionizes the gas in the deject.
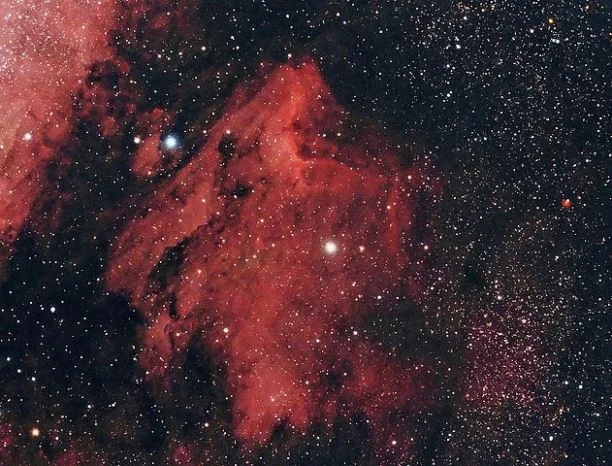

Pelican Nebula, image: Wikimedia Commons/Hewholooks
The nebula is associated with the nearby North America Nebula and is separated from information technology by a large molecular cloud filled with dark dust. The 2 nebulae are about 1,500 low-cal years apart.
The Pelican Nebula is located near the bright star Deneb and can be found to the northeast of the star.
Sadr Region – IC 1318
IC 1318 is an emission nebula formed effectually the star Sadr, Gamma Cygni, located at the intersection of the Northern Cantankerous in Cygnus.
Crescent Nebula – NGC 6888 (Caldwell 27, Sharpless 105)
The Crescent Nebula is an emission nebula formed past the stiff stellar air current of HD 192163 (WR 136), which is a Wolf Rayet star in Cygnus. A Wolf Rayet star is a hot, old, massive star that is apace losing mass by ways of a fast stellar wind.
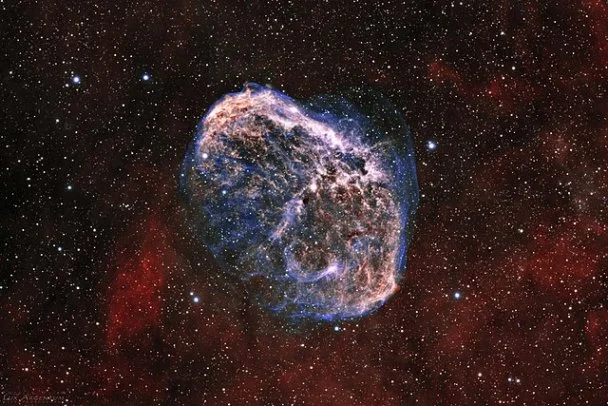

An image of the emission nebula NGC 6888, also known as the Crescent Nebula, in the constellation Cygnus. This object is approximately 5000 light years distant and 26 light years in diameter and is formed by loftier velocity stellar wind from the central star WR 136 colliding with gas previously shed from the star. This object was imaged in hydrogen-alpha and oxygen-III emission lines; red colors are hydrogen, and blue oxygen. Image: Patrick Hsieh (CC BY-SA iv.0)
The shell is a result of the stellar air current from the star colliding with the wind that the star ejected when it evolved into a carmine giant some 400,000 years agone.
The nebula is 18'x12' in size, has an apparent magnitude of vii.four, and is approximately 5,000 calorie-free years distant.
Cygnus Loop (Sharpless 103)
The Cygnus Loop is a large supernova remnant, nearly three degrees beyond in the sky, forming an emission nebula in Cygnus. It is a strong source of soft X-rays.
The arcs of the loop that emit in visible lite are known as the Veil Nebula and the rest of the loop can exist detected in radio, infrared and 10-ray images.
Veil Nebula – NGC 6960, NGC 6992, NGC 6995, NGC 6974, NGC 6979 (IC 1340)
The Veil Nebula is the visual component of the Cygnus Loop. Also known equally the Cirrus Nebula or Filamentary Nebula, it consists of several components: the Western Veil (NGC 6960), the Eastern Veil (NGC 6992, NGC 6995, IC 1340), and Fleming's Triangle (Pickering'southward Triangle).
NGC 6960, the Western Veil, is sometimes as well chosen the Witch's Broom. Information technology forms the western-most office of the nebula. The Eastern Veil consists of iii bright regions – NGC 6996, NGC 6995 and IC 1340.

Portion of the Veil Nebula equally photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope. Image: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage (STScI/Aura)-ESA/Hubble Collaboration
Pickering's Triangle, likewise known every bit Pickering'due south Wedge or Pickering's Triangular Wisp, is a faint region of nebulosity discovered by the American astronomer Williamina Fleming in 1904. It was named after Edward Charles Pickering, the director of the Harvard Observatory, where Fleming made the discovery.
NGC 6974 and NGC 6979 are also regions of nebulosity located in a cloud at the northern border of the nebula. NGC 6979 was discovered by William Herschel, and NGC 6974 past Lord Rosse, a British astronomer.
The Cygnus Loop is about xc lite years in size and approximately 1470 light years distant from World. The estimated historic period of the supernova remnant is between 5,000 and 8,000 years.
Source: https://www.constellation-guide.com/constellation-list/cygnus-constellation/
Posted by: jamesmethery.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Colors Are The Two Stars At The Head Of Cygnus?"
Post a Comment